⏲️ Estimated reading time: 10 min
Seeing “exceeds the maximum upload size” when adding images to WordPress? This step-by-step guide shows every reliable fix cPanel/WHM, php.ini, .htaccess, Nginx/Apache, Multisite limits, and safe image optimization plus verification and troubleshooting to stop the 2 MB cap for good.
How to Fix the “Maximum upload file size: 2 MB” Error in WordPress
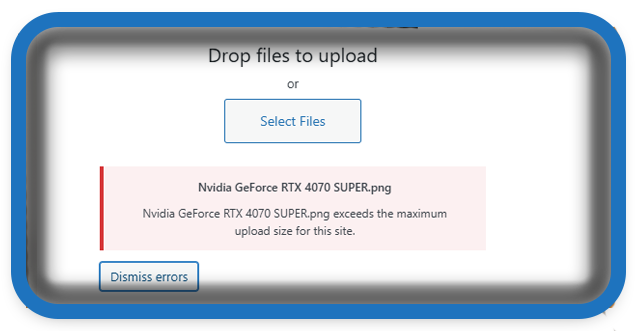
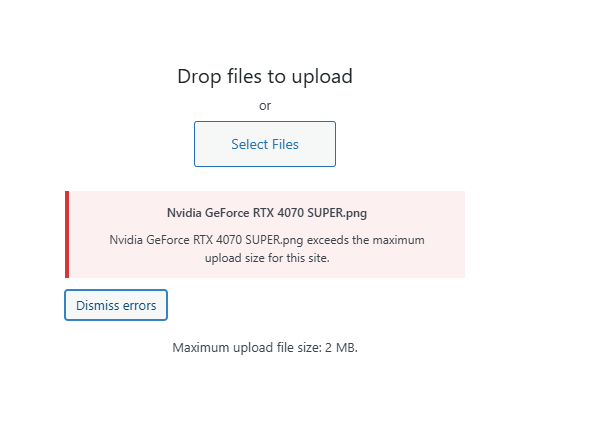
When you try to upload a file in Media → Add New and WordPress throws a pink error box like:
“<filename> exceeds the maximum upload size for this site.”
Maximum upload file size: 2 MB.
…it means your server (PHP and/or web server) is blocking files larger than the configured threshold. You’ll often hit this while uploading PNGs straight from design tools (e.g., GPU box renders, 4K screenshots) or video clips.
This tutorial gives you every working fix from the simplest (host panel toggles) to the most technical (server config). Use the first method you have access to; you don’t have to do all of them.
What Controls the Upload Limit?
Four layers can cap your upload size:
- PHP directives (hard cap)
upload_max_filesize– the size of a single upload.post_max_size– must be ≥upload_max_filesize(form payload).memory_limit– enough headroom to process the file.
- Web server (Apache or Nginx)
- Apache:
LimitRequestBody(rarely used). - Nginx:
client_max_body_size.
- Apache:
- WordPress itself
- Multisite: Network Settings → Max upload file size.
- Some security/performance plugins can also set caps.
- Hosting policy
- Shared hosting may impose an upper bound you can’t exceed without an upgrade.
The fix is to raise the lowest limit among these.
Quick Checklist: What Values Should I Use?
- Small sites:
upload_max_filesize=32M,post_max_size=64M,memory_limit=256M - Media-heavy sites:
upload_max_filesize=64M(or128M),post_max_size=128M(or256M),memory_limit=512M - Timeout safety:
max_execution_time=120,max_input_time=120
Rule of thumb:
post_max_sizeshould be 2×upload_max_filesize.
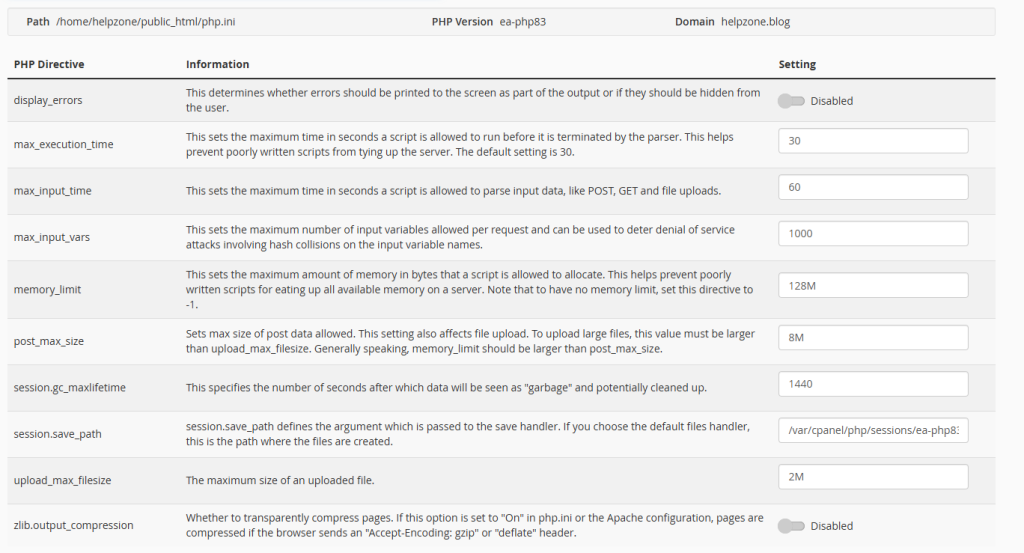
Method 1 – cPanel: MultiPHP INI Editor (Fastest on shared hosting)
If your site uses cPanel (common on AlmaLinux + cPanel/WHM stacks):
- cPanel → Software → MultiPHP INI Editor
- Select your domain from the dropdown.
- Find and set:
upload_max_filesize = 64M post_max_size = 128M memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 120 max_input_time = 120 - Click Apply / Save.
This writes a domain-scoped .user.ini or local PHP config and works instantly on Apache + PHP-FPM handlers commonly used by hosts.
If you have WHM (server admin)
- WHM → MultiPHP INI Editor → Editor Mode → choose the PHP version → set the same directives globally.
- Or WHM → MultiPHP Manager to ensure the domain uses PHP-FPM and the intended PHP version.
Method 2 – Edit .user.ini (Reliable and safe)
If MultiPHP INI Editor is unavailable, create or edit a .user.ini file in your site’s document root (e.g., public_html/ or the WordPress folder):
; .user.ini
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
memory_limit = 512M
max_execution_time = 120
max_input_time = 120
Save, then wait ~1–5 minutes (PHP-FPM caches .user.ini), or restart PHP-FPM if you can.
Method 3 – Edit php.ini (VPS / Dedicated)
On VPS/Root servers (e.g., AlmaLinux):
- Locate your active PHP-FPM pool or global
php.ini. Typical paths:/opt/cpanel/ea-php82/root/etc/php.ini(cPanel EA-PHP)/etc/php.ini(distro default)- Pool overrides in
/opt/cpanel/ea-php82/root/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
- Set:
upload_max_filesize = 64M post_max_size = 128M memory_limit = 512M - Restart PHP-FPM/Apache:
systemctl restart ea-php82-php-fpm.service systemctl restart httpd(Adjust the PHP version/service names to match your server.)
Method 4 – .htaccess (Apache only)
If you’re on Apache and PHP is running as an Apache module/handler that honors .htaccess:
# .htaccess in the WordPress root
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
php_value post_max_size 128M
php_value memory_limit 512M
php_value max_execution_time 120
php_value max_input_time 120
If you get a 500 Internal Server Error, your handler doesn’t allow
php_valuein.htaccess. Remove these lines and use.user.iniinstead.
Method 5 – Nginx: client_max_body_size
If your stack uses Nginx (alone or as a reverse proxy), add to the appropriate context (http, server, or location):
client_max_body_size 128m;
Then reload Nginx:
nginx -t && systemctl reload nginx
You still need PHP limits raised (
upload_max_filesize,post_max_size), otherwise PHP will block uploads.
Method 6 – WordPress Multisite Setting
For Multisite networks:
- Network Admin → Settings → Max upload file size
Set a value in KB (e.g.,131072for 128 MB). - This is an additional cap and won’t override stricter PHP/web-server limits.
Method 7 – Use a Helper Plugin (No server access)
If you can’t edit server files, install a reputable plugin such as:
- Increase Maximum Upload File Size
- WP Maximum Upload File Size
These plugins surface your current limits and, when possible on your host, apply .user.ini style overrides. They can’t bypass strict host caps.
How to Verify the Fix
After applying a change, confirm the new limit:
- WordPress: Media → Add New shows the current “Maximum upload file size” below the drop zone.
- Tools → Site Health → Info → Server exposes PHP values.
- (Optional) Create a temporary
phpinfo.php:<?php phpinfo();Upload it to your root, open it in a browser, and search forupload_max_filesize,post_max_size. Delete this file after checking.
Try uploading the original image again. If it still fails, continue with the troubleshooting below.
Troubleshooting: Still Getting the Error?
- Mismatch between layers
- Ensure
post_max_size≥upload_max_filesize. - If Nginx is in front, set
client_max_body_size. - On Apache, ensure no
LimitRequestBodyexists in a vhost or.htaccess.
- Ensure
- PHP-FPM cache
.user.inichanges can take minutes. Restart PHP-FPM if you can.
- Wrong PHP version
- Your domain might run PHP 8.1 while you edited PHP 8.3’s config. Check MultiPHP Manager for the active version.
- Hosting hard cap
- Some shared plans cap at 32–64 MB. Open a ticket or upgrade.
- Multisite cap
- Increase Network Admin → Settings → Max upload file size.
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
- Classic Nginx symptom. Set
client_max_body_sizeand reload.
- Classic Nginx symptom. Set
- HTTP Error on image processing
- Large images can exhaust memory during thumbnail creation.
- Raise
memory_limit(e.g., 512M) and switch from Imagick to GD (or vice versa) inwp-config.php:// Force GD if Imagick misbehaves define('IMAGE_EDIT_OVERWRITE', true);Or use a plugin to set the editor engine.
Safe Image Practices (Fix the Error and Speed Up Your Site)
Even after raising limits, don’t upload massive raw assets. Oversized images hurt Core Web Vitals (LCP/CLS) and hosting costs.
1) Choose the right format
- WebP: Best default for photos/graphics (great compression).
- PNG: Only for transparency or pixel-perfect UI elements.
- JPEG: Okay for photos if you can’t use WebP yet.
- SVG: For simple logos/icons (allow securely with an SVG sanitizer plugin).
2) Resize before upload
- For featured images in most themes, 1200–1600 px width is enough.
- For full-width hero images on 4K, 1920–2560 px is plenty.
3) Compress
- Desktop tools: Squoosh, ImageOptim, TinyPNG/TinyJPG.
- WordPress plugins (server-side or API): Imagify, ShortPixel, Smush.
4) Automate conversion to WebP/AVIF
- Use WebP Express, EWWW Image Optimizer, or your CDN (Cloudflare Polish, Bunny CDN Optimizer).
5) Respect DPR (retina)
- You rarely need more than 2× pixel density. Don’t upload 8K assets for a 300-px logo.
Security & Stability Notes
- Don’t set limits to something absurd (e.g.,
2G). Higher limits widen attack surfaces and intensify resource spikes. - Backups: Changes to
php.ini,.htaccess, or Nginx conf should be backed up and version-controlled if possible. - Permissions: Ensure your
.user.iniand.htaccesshave standard perms (644) and are owned by the correct user. - Clean up: Remove temporary
phpinfo.phpfiles immediately after use.
Real-World Example: From 2 MB to 128 MB on cPanel (AlmaLinux)
- Log in to cPanel.
- Open MultiPHP INI Editor → Editor Mode (or Basic Mode if available).
- Select the domain and set:
upload_max_filesize = 64M post_max_size = 128M memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 120 - Save.
- (If you also run Nginx proxy) ask your host or, on VPS, set
client_max_body_size 128m;and reload Nginx. - Verify in Media → Add New that “Maximum upload file size” reflects the new value.
- Re-upload your Nvidia GeForce RTX PNG. Done.
Optional: WP-CLI One-Minute Health Check (VPS)
If you have SSH:
# Check active PHP version and limits via php -i
php -i | egrep 'PHP Version|upload_max_filesize|post_max_size|memory_limit'
# On EA-PHP with cPanel, also check the domain handler
grep -R "php-fpm" /etc/apache2/conf.d/ | head
This quickly confirms whether you edited the correct PHP runtime.
When You Should Not Raise the Limit
- Your users will upload files publicly (forms/members). Instead, restrict roles, use file type allowlists, and throttle size to reduce abuse.
- Your hosting plan is tiny and you’re close to inode or space limits. Upgrading the plan or using an external object storage (S3, Wasabi, Bunny) may be wiser.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I change the limit from wp-config.php?
Not reliably. ini_set() calls in wp-config.php are often blocked by PHP-FPM. Prefer .user.ini, MultiPHP INI Editor, or php.ini.
Q2: My host says the cap is 32 MB. What now?
You can still compress/resize images before upload. For videos or huge media, store files on YouTube/Vimeo or object storage and embed.
Q3: I increased limits but still get “HTTP error”.
That’s usually image processing (Imagick/GD) running out of memory or time. Raise memory_limit, and try the other image editor engine or an optimization plugin.
Q4: Do I need to restart the server?
.user.iniusually auto-reloads within minutes.php.ini/FPM pool changes require PHP-FPM restart.- Nginx changes require Nginx reload.
- Apache
.htaccessis immediate.
Q5: Is there any SEO impact?
Indirectly yes: oversized images slow pages and hurt Core Web Vitals. Fix the cap but still keep images lean (use WebP, responsive sizes).
Final Takeaway
The “Maximum upload file size: 2 MB” error is a sign that one of your limits is too low usually PHP’s upload_max_filesize or post_max_size. On cPanel hosting, the MultiPHP INI Editor or a simple .user.ini file solves it in minutes. On VPS, update php.ini and (if using Nginx) client_max_body_size. After raising limits, verify in Media → Add New, then adopt smart image optimization so your site stays fast and stable. Fix the cap once then keep uploads efficient forever.
🔔 For more tutorials like this, consider subscribing to our blog.
📩 Do you have questions or suggestions? Leave a comment or contact us!
🏷️ Tags: WordPress upload limit, php.ini, .user.ini, cPanel MultiPHP INI Editor, Nginx client_max_body_size, Apache .htaccess, WordPress Multisite, image optimization, HTTP error upload, PHP memory limit
📢 Hashtags: #WordPress, #UploadError, #cPanel, #PHPINI, #Nginx, #Apache, #WebHosting, #ImageOptimization, #SiteHealth, #WPAdmin
Only logged-in users can submit reports.
Discover more from HelpZone
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.